Navigating the Maze: A Comprehensive Guide to Enterprise Architecture Tool Selection
The CIO’s Strategy for Managing Shadow IT Risks

Introduction
In today’s digital age, organizations are constantly facing new challenges when it comes to managing their IT infrastructure. One of the biggest challenges that CIOs (Chief Information Officers) face is the presence of shadow IT. Shadow IT refers to the use of unsanctioned or unauthorized IT systems, software, and services within an organization. These can include cloud applications, mobile apps, and other technology solutions that are not approved or managed by the IT department.
Shadow IT poses significant risks to organizations, including data breaches, compliance violations, and operational inefficiencies. In this article, we will explore the risks associated with shadow IT and discuss strategies that CIOs can implement to control and integrate unsanctioned IT usage. We will examine each stage of the risk lifecycle and provide actionable insights for CIOs to mitigate these risks effectively.
The Risks of Shadow IT
-
Data Security Risks
- One of the most significant risks of shadow IT is the potential compromise of data security. When employees use unsanctioned IT systems, it becomes challenging for the IT department to ensure that proper security measures are in place. This can lead to data breaches, unauthorized access to sensitive information, and the loss of valuable data. CIOs must prioritize data security and implement robust measures to protect organizational data from such risks.
-
Compliance Risks
- Shadow IT can also pose compliance risks for organizations. Many industries have strict regulations and compliance requirements that organizations must adhere to. When employees use unsanctioned IT systems, it becomes difficult to ensure that these systems comply with industry regulations. This can result in compliance violations and legal consequences for the organization. CIOs should work closely with legal and compliance teams to develop strategies that ensure adherence to regulatory requirements.
-
Operational Risks
- Unsanctioned IT usage can lead to operational inefficiencies within an organization. When employees use different systems and software that are not integrated with the organization’s IT infrastructure, it can result in data silos, duplication of efforts, and decreased productivity. CIOs should focus on streamlining IT processes and providing employees with approved and integrated IT solutions to minimize operational risks.
Strategies for Managing Shadow IT Risks
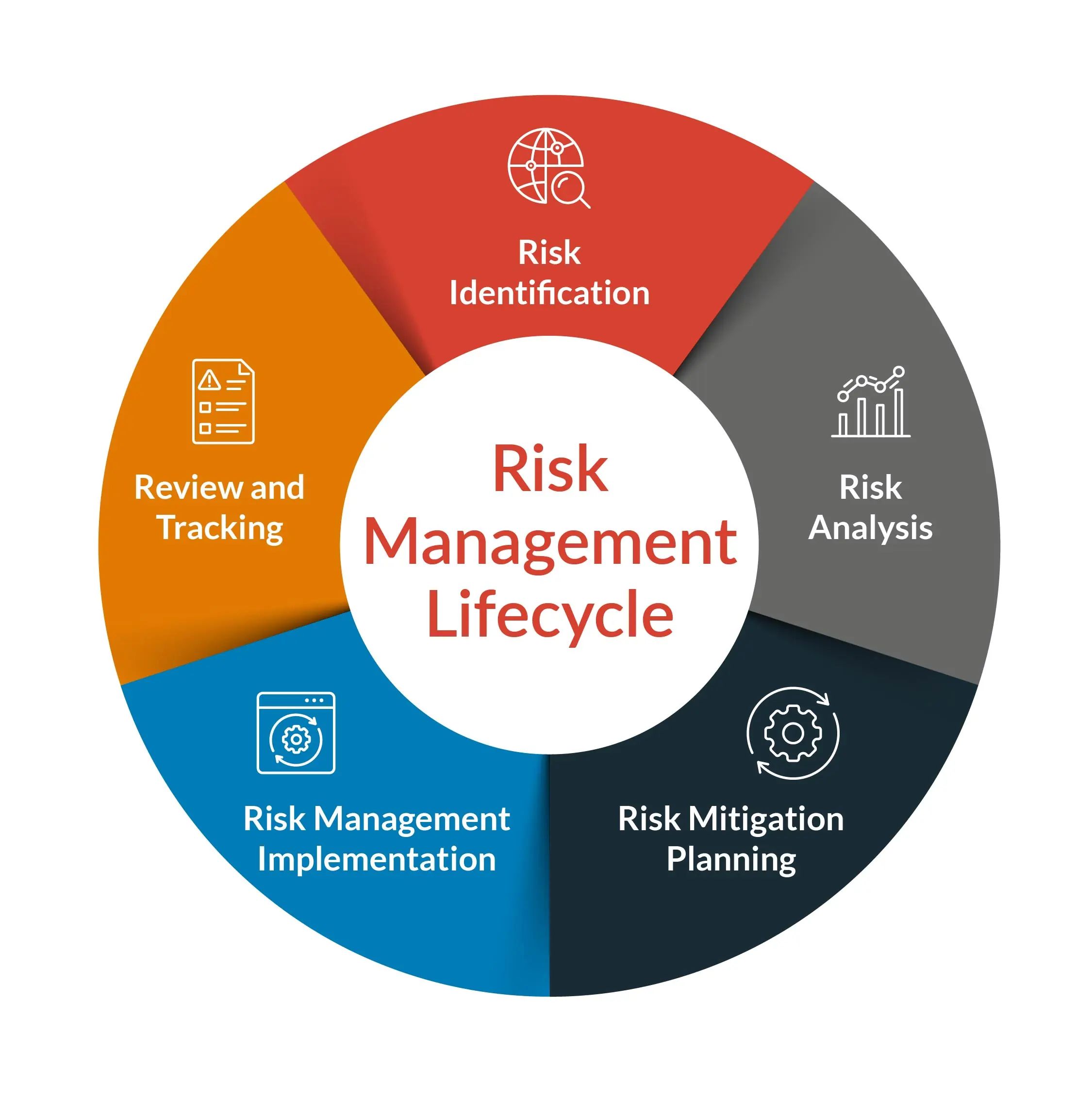
To effectively manage shadow IT risks, CIOs need to implement a comprehensive strategy that addresses each stage of the risk lifecycle. Let’s explore these stages and the corresponding strategies:
-
Risk Identification
- Conduct regular audits and assessments to identify unauthorized IT systems and software.
- Implement network monitoring tools to detect and track unsanctioned IT usage.
- Encourage employees to report any unsanctioned IT usage they come across.
-
Risk Assessment
- Analyze the security vulnerabilities and compliance implications of unsanctioned IT systems.
- Evaluate the operational impact of shadow IT on productivity and efficiency.
- Prioritize risks based on their severity and potential impact on the organization.
-
Risk Mitigation
- Establish clear IT policies and guidelines that outline approved systems and software.
- Educate employees about the risks associated with shadow IT and the importance of adhering to IT policies.
- Implement robust security measures, such as access controls and encryption, to protect organizational data.
-
Risk Monitoring
- Implement real-time monitoring tools to detect and respond to unsanctioned IT usage.
- Regularly review and update IT policies and guidelines to adapt to changing technology trends.
- Conduct periodic audits to ensure compliance with IT policies and identify any new instances of shadow IT.
-
Risk Response
- Establish incident response protocols to address and contain shadow IT incidents.
- Collaborate with legal and compliance teams to handle any regulatory or legal implications.
- Learn from past incidents and update risk management strategies to prevent future occurrences.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q1: What is shadow IT?
Shadow IT refers to the use of unsanctioned or unauthorized IT systems, software, and services within an organization. These can include cloud applications, mobile apps, and other technology solutions that are not approved or managed by the IT department.
Q2: What are the potential risks of shadow IT?
Shadow IT poses several risks to organizations, including:
-
Data security risks: When employees use unsanctioned IT systems, it becomes challenging to ensure proper security measures are in place, leading to data breaches and unauthorized access to sensitive information.
-
Compliance risks: Shadow IT can result in compliance violations as unsanctioned systems may not adhere to industry regulations and standards, leading to legal consequences for the organization.
-
Operational risks: Unsanctioned IT usage can lead to operational inefficiencies, such as data silos, duplication of efforts, and decreased productivity.
Q3: How can CIOs identify shadow IT within their organization?
CIOs can employ various strategies to identify shadow IT:
- Conduct regular audits and assessments to identify unauthorized IT systems and software.
- Implement network monitoring tools to detect and track unsanctioned IT usage.
- Encourage employees to report any unsanctioned IT usage they come across.
Q4: What strategies can CIOs implement to mitigate shadow IT risks?
CIOs can implement the following strategies to mitigate shadow IT risks:
- Establish clear IT policies and guidelines that outline approved systems and software.
- Educate employees about the risks associated with shadow IT and the importance of adhering to IT policies.
- Implement robust security measures, such as access controls and encryption, to protect organizational data.
Q5: How can CIOs monitor and respond to shadow IT incidents?
CIOs can monitor and respond to shadow IT incidents by:
- Implementing real-time monitoring tools to detect and respond to unsanctioned IT usage.
- Regularly reviewing and updating IT policies and guidelines to adapt to changing technology trends.
- Establishing incident response protocols to address and contain shadow IT incidents.
Conclusion
Managing shadow IT risks is a critical task for CIOs in today’s digital landscape. By identifying, assessing, mitigating, monitoring, and responding to shadow IT risks, CIOs can effectively control and integrate unsanctioned IT usage within their organizations. By prioritizing data security, compliance, and operational efficiency, CIOs can ensure that their organizations are well-equipped to navigate the challenges posed by shadow IT and safeguard their valuable assets.
Remember, staying proactive and continuously evolving your risk management strategies is key to successfully managing shadow IT risks. With a comprehensive approach and a focus on collaboration between IT, legal, and compliance teams, CIOs can minimize the impact of shadow IT and protect their organizations from potential harm.
So, embrace the challenge of managing shadow IT risks and empower your organization to thrive in the digital era!