Big Data and Modern Architecture: Building Scalable Systems
February 12, 2024 in Data Architecture, artificial intelligence6 minutes
This article discusses the principles of building scalable data architectures to effectively harness big data. It explores big data systems, data storage, processing technologies, integration, and governance best practices. Organizations can unlock business value by embracing modern architecture design.
Big Data and Modern Architecture: Building Scalable Systems

Introduction
In today’s digital age, data is being generated at an unprecedented rate. From social media interactions to online transactions, every action we take leaves a digital footprint. This massive influx of data has given rise to the field of big data, which focuses on extracting valuable insights from vast and complex datasets. However, working with big data requires more than just powerful hardware and storage capabilities. It demands a well-designed data architecture that can handle the volume, velocity, and variety of data being generated. In this article, we will explore the principles of big data systems and delve into the intricacies of designing scalable data architectures.
Understanding Big Data Systems
What is Big Data?
Big data refers to datasets that are too large and complex to be processed using traditional data processing techniques. These datasets are characterized by the three Vs: volume, velocity, and variety.
Volume: Big data systems deal with massive volumes of data, often ranging from terabytes to petabytes or even exabytes. Traditional databases are ill-equipped to handle such large datasets efficiently. Most organizations now collect data in the order of petabytes.
Velocity: Big data is generated at a high velocity, with data being produced in real-time or near real-time from sensors and IoT devices. This requires systems that can ingest, process, and analyze data at rapid pace of a few milliseconds.
Variety: Big data comes in various formats and structures, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. This includes text, images, videos, social media posts, sensor data, and more. Over 80% of big data is unstructured like text, audio and video files.
The Need for Scalable Systems
To effectively work with big data, organizations need scalable systems that can grow and adapt to their evolving needs. Scalability refers to the ability of a system to handle increasing amounts of data, users, and workload without sacrificing performance. A scalable data architecture ensures that as data volumes grow, the system can seamlessly accommodate the additional load without experiencing bottlenecks or performance degradation.
Designing Scalable Data Architectures
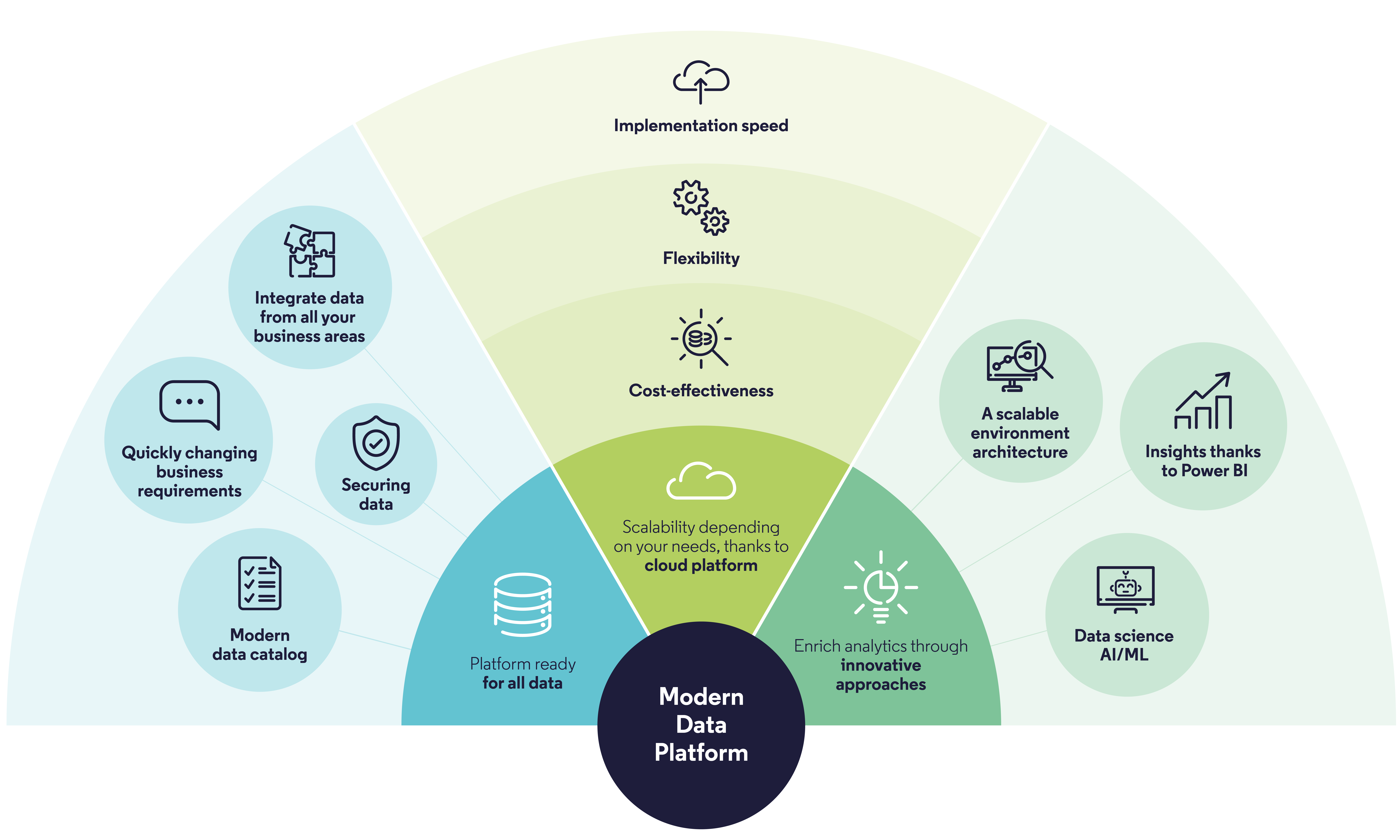
Data Storage and Management
One of the key aspects of designing a scalable data architecture is selecting the appropriate data storage and management technologies. Traditional relational databases, while reliable and mature, may not be the best fit for big data scenarios. Instead, organizations often turn to distributed storage systems like Apache Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS) or cloud-based solutions like Amazon S3 or Google Cloud Storage.
These distributed storage systems offer the advantage of horizontal scalability, allowing organizations to add more storage nodes as data volumes increase. Additionally, they provide fault tolerance and high availability, ensuring that data remains accessible even in the event of hardware failures. Over 70% of organizations use HDFS for storing petabytes of data.
Data Processing and Analysis
Once the data is stored, the next step is to process and analyze it to extract meaningful insights. This is where technologies like Apache Spark, Apache Flink, or Apache Hadoop come into play. These frameworks enable distributed data processing, allowing organizations to parallelize computations across multiple nodes in a cluster.
By distributing the processing workload, these systems can handle large-scale data processing tasks efficiently in parallel. They provide fault tolerance, automatic data partitioning, and built-in mechanisms for data parallelism, making them ideal for big data processing. Apache Spark is used by over 70% of organizations for batch and stream processing of petabytes of data.
Data Integration and Orchestration
In a big data ecosystem, data often resides in various sources and formats. To make sense of this disparate data, organizations need to integrate and orchestrate it effectively. This involves extracting data from different sources, transforming it into a unified format, and loading it into the target system.
Technologies like Apache Kafka, Apache NiFi, or Apache Airflow can be used for data integration and orchestration. These tools provide capabilities for data ingestion, data transformation, and workflow management, ensuring a smooth and streamlined data pipeline. Apache Kafka is used for real-time ingestion and transformation of over 50 billion records per day.
Data Governance and Security
With the increasing importance of data privacy and security, organizations must prioritize data governance and security in their data architectures. This involves implementing access controls, encryption mechanisms, and data governance policies to protect sensitive data.
Tools like Apache Ranger or Apache Atlas can assist in enforcing data governance policies, while technologies like Apache Knox or Apache Sentry can provide secure access to data resources. Over 90% of organizations use Apache Ranger for access control of sensitive data.
FAQ
What are the benefits of using big data systems? Big data systems offer several benefits, including the ability to process and analyze large volumes of data, uncover valuable insights, make data-driven decisions, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
How can organizations ensure the scalability of their data architectures? To ensure scalability, organizations should adopt distributed storage systems, use technologies for distributed data processing, implement data integration and orchestration tools, and prioritize data governance and security.
Are there any challenges associated with big data systems? Yes, big data systems come with their own set of challenges. These include data quality issues, data integration complexities, managing the velocity of incoming data, and ensuring data privacy and security.
What are some popular big data technologies? Some popular big data technologies include Apache Hadoop, Apache Spark, Apache Kafka, Apache Flink, and cloud-based solutions like Amazon S3 and Google Cloud Storage.
How can organizations leverage big data for business success? By harnessing the power of big data, organizations can gain valuable insights into customer behavior, optimize business processes, improve decision-making, enhance customer experiences, and drive innovation.
Conclusion
In the era of big data, organizations must adapt to the challenges and opportunities presented by vast and complex datasets. By designing scalable data architectures, organizations can effectively manage and leverage big data to gain valuable insights and drive business success. From selecting the right storage and processing technologies to ensuring data governance and security, every aspect of the data architecture plays a crucial role in unlocking the potential of big data. Embracing the principles of big data systems and modern architecture is key to building scalable systems that can meet the ever-growing demands of the digital age.
Remember, the world of big data is constantly evolving, and staying up-to-date with the latest technologies and best practices is essential for organizations to stay ahead of the competition. So, embrace the power of big data, design scalable data architectures, and unlock the full potential of your organization’s data.