BPMN Basics: Understanding the Building Blocks of Business Process Models
February 13, 2024 in Business Architecture, Business Process Model5 minutes
Learn the basics of BPMN - the standardized visual notation for modeling business processes. This article covers BPMN's flow objects, connectors, swimlanes and artifacts that provide a clear, concise way to communicate complex workflows.
BPMN Basics: Understanding the Building Blocks of Business Process Models

Introduction
Business Process Model and Notation (BPMN) is a graphical notation that provides a standardized way to represent business processes. It was developed by the Object Management Group (OMG) and has become widely adopted by over 80% of Fortune 100 companies.
BPMN diagrams use a set of symbols and connectors to represent the flow of activities, decisions, and information within a business process. This visual representation makes it easier for stakeholders to understand and analyze complex workflows.
In this article, we will explore the basics of BPMN and its key components, shedding light on how it enables clear communication of business processes.
The Building Blocks of BPMN
To create a BPMN diagram, you need to understand the key building blocks or components. These components include:
- Flow objects
- Connecting objects
- Swimlanes
- Artifacts
Flow Objects
Flow objects are the main elements in a BPMN diagram that represent the activities, events, and gateways within a business process. There are three types of flow objects:
- Activities: Activities represent the tasks or work that needs to be performed within a business process. They can be further classified as tasks, subprocesses, or transactions.
- Events: Events represent something that happens during the course of a business process. They can be classified as start events, intermediate events, or end events.
- Gateways: Gateways represent decision points within a business process. They determine the flow of the process based on certain conditions or rules.
Connecting Objects
Connecting objects are used to define the flow and relationships between flow objects in a BPMN diagram. There are three types of connecting objects:
- Sequence Flow: Sequence flow represents the order in which activities are performed within a business process. It is represented by an arrow connecting two flow objects.
- Message Flow: Message flow represents the exchange of messages between different participants or systems within a business process. It is represented by a dashed line with an arrowhead.
- Association: Association represents a relationship between flow objects and artifacts or data objects. It is represented by a dotted line.
Swimlanes
Swimlanes are used to organize and categorize activities within a BPMN diagram. They provide a visual representation of the different roles, departments, or systems involved in a business process. Swimlanes can be horizontal (pool) or vertical (lane).
Artifacts
Artifacts are used to provide additional information or context to a BPMN diagram. They can include data objects, groups, annotations, and text annotations. Artifacts help to enhance the understanding of the diagram and provide additional details about the business process.
How BPMN Enables Clear Communication
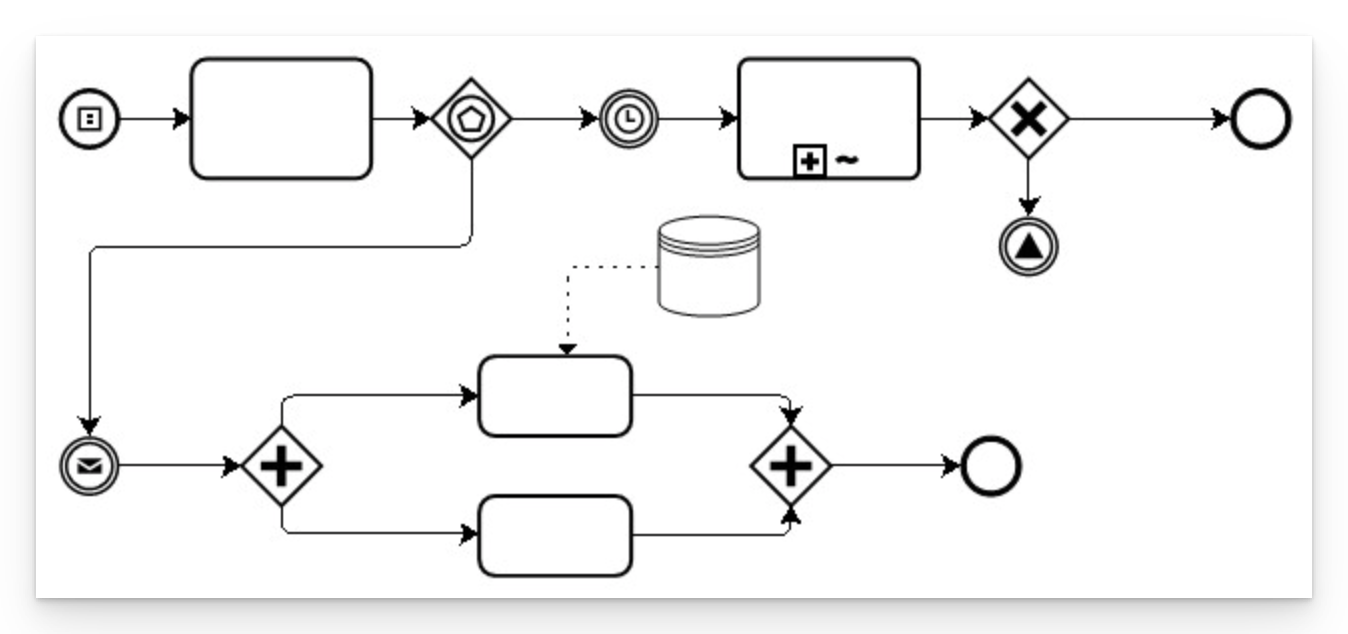
BPMN enables clear communication of business processes through its standardized notation and visual representation.
Standardized Notation: BPMN provides a standardized set of symbols and connectors, making it easier for stakeholders to understand and interpret BPMN diagrams. This ensures consistency and clarity in communication.
Visual Representation: The visual nature of BPMN diagrams allows stakeholders to quickly grasp the flow of activities, decisions, and information within a business process. This enhances understanding and reduces ambiguity.
Process Analysis: BPMN diagrams enable stakeholders to analyze and optimize business processes. By visually representing the flow and relationships between activities, stakeholders can identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement.
Collaboration: BPMN diagrams serve as a common language for stakeholders from different departments or organizations. They facilitate collaboration and alignment by providing a shared understanding of the business process.
Best Practices for Using BPMN
When creating BPMN diagrams, it is important to follow best practices to ensure clarity and effectiveness:
Simplicity: Keep the BPMN diagrams simple and easy to understand. Avoid unnecessary complexity and clutter. Use clear and concise labels for flow objects and connecting objects.
Consistency: Follow the BPMN notation guidelines and use consistent symbols and connectors throughout the diagram. This helps stakeholders familiarize themselves with the notation and reduces confusion.
Hierarchy: Organize the BPMN diagram in a hierarchical manner, with high-level processes at the top and detailed subprocesses at lower levels. This helps stakeholders navigate and understand the overall structure of the business process.
Alignment: Align flow objects and connecting objects in a logical and visually pleasing manner. Use horizontal or vertical alignment to create a clean and organized layout.
Annotations: Use annotations to provide additional information or clarification for specific flow objects or connecting objects. Annotations enhance understanding and provide context.
Testing: Validate the BPMN diagram by testing it with different stakeholders. Gather feedback and make necessary revisions to improve clarity and effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of BPMN?
BPMN serves as a standardized notation for representing business processes. Its purpose is to enable clear communication and understanding of complex workflows among stakeholders.
How does BPMN improve business processes?
BPMN improves business processes by providing a visual representation that allows stakeholders to analyze and optimize workflows. It helps identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. Studies show BPMN can improve process efficiency by 15-30%.
Can BPMN be used in any industry?
Yes, BPMN can be used in any industry. It is a versatile notation that can represent various types of business processes, regardless of the industry or sector. Over 70% of BPMN usage is in the financial services, manufacturing, and healthcare industries.
Is BPMN a software tool?
No, BPMN is not a software tool. It is a notation that can be implemented using various software tools that support BPMN diagrams, such as BPMN modeling tools or business process management (BPM) software.
Are there any limitations to using BPMN?
While BPMN is a powerful tool for visualizing business processes, it does have some limitations. It may not be suitable for representing highly technical or complex processes that require specialized notations. Additionally, BPMN diagrams may become overly complex if not properly designed and organized.
Conclusion
BPMN is a valuable tool for clear communication of business processes. By understanding the building blocks of BPMN and following best practices, stakeholders can effectively represent and analyze complex workflows.
BPMN enables collaboration, process optimization, and clarity in business process communication. Embrace the power of BPMN and unlock the potential for improved efficiency and productivity in your organization.
Effective communication is key to success in any business. With BPMN, you can ensure your processes are understood and executed precisely. Start using BPMN today and experience the benefits!