Business Intelligence Architecture: Unleashing the Potential of Data
March 6, 2024 in CIO, Business Architecture7 minutes
Unlock the power of data with Business Intelligence Architecture. Learn how a well-designed BI architecture can transform raw data into meaningful insights, driving informed decision-making, optimizing operations, and fueling business growth. Discover the components, benefits, and emerging trends in BI architecture.
Business Intelligence Architecture: Unleashing the Potential of Data
In the contemporary, rapid-paced, and data-centric business environment, companies are persistently in pursuit of methods to secure a competitive edge. One of the most potent strategies to achieve this is by tapping into the potential of data through Business Intelligence (BI) architecture. By implementing a meticulously designed BI architecture, organizations can metamorphose raw data into insightful knowledge, driving informed decision-making, enhancing operations, and stimulating business expansion.
Understanding Business Intelligence Architecture
Business Intelligence Architecture pertains to the structural framework and infrastructure that facilitates the gathering, assimilation, storage, examination, and visualization of data within an organization. It envelops the instruments, technologies, procedures, and strategies utilized to convert raw data into actionable insights. A sturdy BI architecture guarantees that data is accessible, precise, and dependable, empowering stakeholders at all strata to make data-influenced decisions.
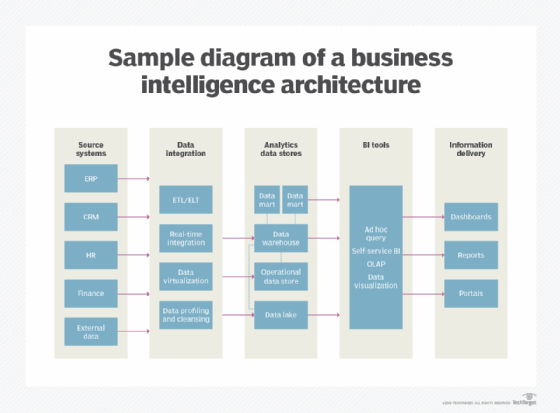
Key Components of Business Intelligence Architecture
A holistic BI architecture comprises several pivotal components that function together harmoniously to deliver invaluable insights. Let’s delve into each component in detail:
1. Data Sources:
Data sources serve as the cornerstone of any BI architecture. They can encompass internal systems such as ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), CRM (Customer Relationship Management), and HRM (Human Resource Management) systems, as well as external resources like social media platforms, market research reports, and public datasets. It is indispensable to pinpoint and incorporate pertinent data sources to ensure an exhaustive view of the business panorama.
2. Data Integration:
Data integration entails the process of amalgamating data from diverse sources into a uniform and coherent format. This phase guarantees that data is accurate, comprehensive, and primed for analysis. ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) tools are frequently employed to retrieve data from different sources, modify it into a standardized format, and upload it into a data warehouse or data mart.
3. Data Storage:
Data storage is an indispensable component of BI architecture. It involves the organization and storage of data in a structured manner to expedite efficient retrieval and analysis. Data can be stored in a data warehouse, which is a centralized repository that stores historical and current data from various sources. Alternatively, data marts can be utilized to store specific subsets of data tailored to the needs of different business units.
4. Data Modeling:
Data modeling is the process of blueprinting the structure and relationships of data within a BI architecture. It requires creating logical and physical data models that define how data is organized, stored, and accessed. Data modeling ensures that data is structured in a way that supports efficient querying, reporting, and analysis.
5. Data Analysis:
Data analysis forms the crux of BI architecture. It involves implementing various analytical techniques to glean insights from data. This can include descriptive analytics, which focuses on comprehending what transpired, diagnostic analytics, which aims to ascertain why something occurred, predictive analytics, which anticipates future outcomes, and prescriptive analytics, which offers recommendations for optimal decision-making.
6. Data Visualization:
Data visualization is the process of portraying data in a visual format, such as charts, graphs, and dashboards. It empowers stakeholders to comprehend complex data patterns and trends swiftly. Effective data visualization enhances data comprehension and facilitates the communication of insights across the organization.
7. Reporting and Dashboards:
Reporting and dashboards provide a consolidated view of key performance indicators (KPIs) and metrics. They enable stakeholders to monitor business performance, track progress towards goals, and identify areas for improvement. Interactive dashboards allow users to drill down into specific data points and explore data in real-time.
Advantages of Implementing Business Intelligence Architecture
Implementing a robust BI architecture proffers myriad benefits for organizations. Some of the principal advantages include:
Data-Driven Decision Making: BI architecture equips organizations to make well-informed decisions based on accurate and timely data. It eradicates conjecture and enables stakeholders to depend on data-driven insights. According to a report by Dresner Advisory Services, 53% of enterprises that adopt BI state that it significantly improves their decision-making capabilities.
Enhanced Operational Efficiency: By optimizing data integration, storage, and analysis processes, BI architecture boosts operational efficiency. It decreases manual exertion, minimizes errors, and enables quicker access to vital information. A study by Nucleus Research indicates that organizations achieve an average return on investment (ROI) of $13.01 for every dollar spent on BI.
Amplified Business Performance: BI architecture enables organizations to monitor KPIs, track performance, and identify areas for improvement. It fosters proactive decision-making and aids in propelling business growth. A survey by Aberdeen Group reveals that companies using BI witness a 28% increase in revenue growth.
Competitive Advantage: Organizations that effectively harness BI architecture gain a competitive edge. They can discern market trends, customer preferences, and emerging opportunities, empowering them to outpace the competition. According to a report by Gartner, organizations that leverage analytics are five times more likely to make faster decisions than their competitors.
Cost Optimization: BI architecture assists organizations in identifying cost-saving opportunities by analyzing data and pinpointing areas of inefficiency. It enables better resource allocation and optimization of business processes. A study by IDC states that organizations can achieve up to a 10% reduction in operational costs through the use of BI.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What are the crucial considerations for designing a Business Intelligence architecture?
Designing a successful BI architecture necessitates meticulous planning and consideration. Some vital considerations include identifying relevant data sources, ensuring data quality and integrity, selecting appropriate tools and technologies, and aligning the architecture with business goals and objectives. It is also essential to involve stakeholders from different departments to understand their specific data needs and requirements.
2. How can data governance be integrated into a Business Intelligence architecture?
Data governance plays a crucial role in ensuring data quality, security, and compliance within a BI architecture. It involves establishing policies, processes, and controls for data management. Data governance frameworks can be integrated into the BI architecture to enforce data standards, define data ownership, and establish data access and security protocols.
3. What are some best practices for data visualization in a Business Intelligence architecture?
When it comes to data visualization in BI architecture, it is essential to follow best practices to maximize the impact and effectiveness of visualizations. Some key practices include selecting the appropriate visualization types for the data, keeping visualizations simple and uncluttered, using color and formatting effectively, and providing context and annotations to aid interpretation.
4. How can Business Intelligence architecture support self-service analytics?
Self-service analytics allows users to explore and analyze data independently without relying on IT or data analysts. BI architecture can support self-service analytics by providing user-friendly tools and interfaces, ensuring data accessibility and availability, and implementing security measures to protect sensitive data. It also involves providing training and support to users to enable them to leverage the full potential of self-service analytics.
5. What are the emerging trends in Business Intelligence architecture?
Business Intelligence architecture is constantly evolving to keep up with technological advancements and changing business needs. Some emerging trends in BI architecture include the adoption of cloud-based BI solutions, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning for advanced analytics, the use of natural language processing for querying and reporting, and the incorporation of real-time data streaming and analysis capabilities.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Business Intelligence architecture is a potent instrument that enables organizations to unleash the full potential of their data. By implementing a well-designed BI architecture, businesses can acquire valuable insights, make well-informed decisions, and stimulate growth. It is crucial to consider the various components of BI architecture, such as data integration, storage, analysis, and visualization, to ensure a comprehensive and effective solution. With the right BI architecture in place, organizations can harness the power of data and stay ahead in today’s competitive business landscape.
Remember, the key to success lies in leveraging the right tools, technologies, and methodologies to transform data into actionable insights. So, embrace the power of Business Intelligence architecture and unlock the true potential of your data-driven business.
Find more about our CIO Insights on Blog
Find more about our conprehensive Enterprise Architecture Guide