Data Lake Architecture: A Comprehensive Guide
March 12, 2024 in Data architecture14 minutes
Unlock the full potential of your data with Data Lake Architecture. This comprehensive guide explores data ingestion, storage, processing, governance, benefits, best practices, real-world success stories, and future trends, empowering you to harness the value of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data for advanced analytics and data-driven decision-making.
Data Lake Architecture: A Comprehensive Guide
Introduction
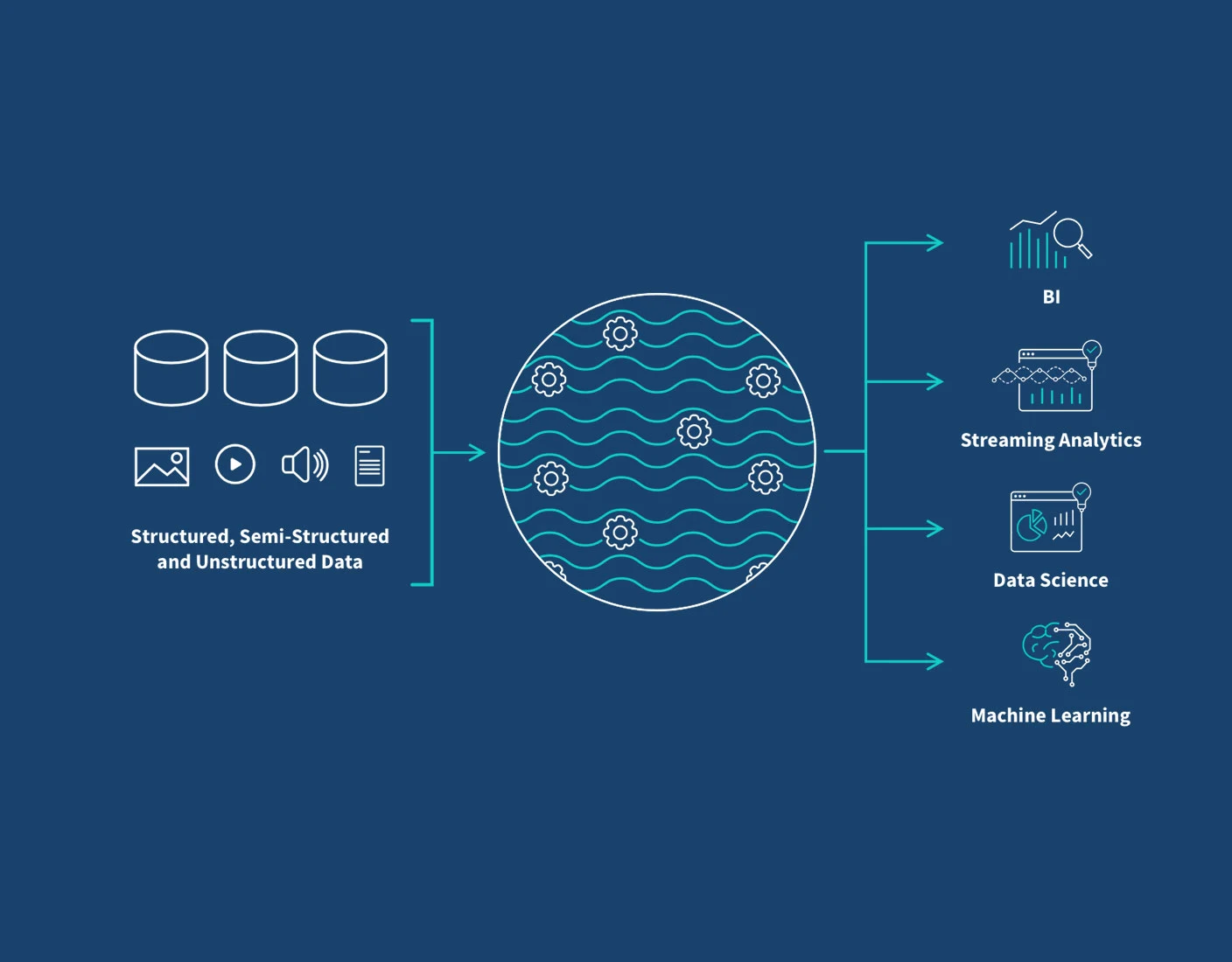
In today’s data-driven world, organizations are constantly collecting and analyzing vast amounts of data to gain valuable insights and make informed decisions. According to a study by IDC, the global datasphere is expected to grow from 33 zettabytes in 2018 to 175 zettabytes by 2025. To effectively manage and utilize this data, a robust architecture is required. One such architecture that has gained significant popularity is the Data Lake Architecture. In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of Data Lake Architecture, its components, benefits, and best practices. Get ready to dive into the world of Data Lake Architecture and unlock the full potential of your data!
Table of Contents
- What is Data Lake Architecture?
- Components of Data Lake Architecture
- 2.1 Data Ingestion
- 2.2 Data Storage
- 2.3 Data Processing
- 2.4 Data Governance and Security
- Benefits of Data Lake Architecture
- Best Practices for Implementing Data Lake Architecture
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
- 5.1 What is the difference between a Data Lake and a Data Warehouse?
- 5.2 How does Data Lake Architecture support big data analytics?
- 5.3 What are the challenges of implementing Data Lake Architecture?
- 5.4 How can data governance be ensured in a Data Lake?
- 5.5 What are some popular tools for implementing Data Lake Architecture?
- Real-World Success Stories
- Future of Data Lake Architecture
- Conclusion
1. What is Data Lake Architecture?
Data Lake Architecture is a modern data storage and processing framework that allows organizations to store and analyze large volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. Unlike traditional data storage systems like data warehouses, which follow a structured approach, Data Lake Architecture provides a more flexible and scalable solution for handling diverse data types.
In a Data Lake Architecture, data is stored in its raw form, without the need for predefined schemas or transformations. This raw data can then be processed and transformed as needed, enabling organizations to derive valuable insights and perform advanced analytics.
According to a survey by Gartner, by 2022, 90% of corporate strategies will explicitly mention information as a critical enterprise asset and analytics as an essential competency. Data Lake Architecture empowers organizations to leverage their data assets effectively and gain a competitive edge.
2. Components of Data Lake Architecture
Data Lake Architecture consists of several key components that work together to enable efficient data storage, processing, and analysis. Let’s explore each component in detail:
2.1 Data Ingestion
Data Ingestion is the process of collecting and importing data from various sources into the Data Lake. This component ensures that data from different systems, such as databases, applications, IoT devices, and external sources, can be seamlessly integrated into the Data Lake.
To facilitate data ingestion, organizations can leverage various tools and technologies such as:
- Apache Kafka: A distributed streaming platform for real-time data ingestion and processing.
- Apache NiFi: An open-source data integration tool that enables data extraction, transformation, and loading (ETL).
- Custom-built connectors: Tailored solutions for specific data sources and formats.
A study by Forrester found that organizations using streaming analytics and real-time data ingestion can experience a 66% increase in customer satisfaction and a 30% reduction in operational costs.
2.2 Data Storage
Data Storage is a crucial component of Data Lake Architecture, as it involves the physical storage of data in its raw form. Unlike traditional databases or data warehouses, which require predefined schemas, Data Lake Architecture allows for the storage of diverse data types without any predefined structure.
Commonly used storage technologies in Data Lake Architecture include:
- Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS): An open-source, scalable, and fault-tolerant storage system for large datasets.
- Amazon S3: A scalable and secure object storage service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS).
- Azure Data Lake Storage: A secure and scalable data lake storage service offered by Microsoft Azure.
- Google Cloud Storage: A cost-effective and durable object storage service provided by Google Cloud Platform.
According to a report by MarketsandMarkets, the global data lake market size is expected to grow from USD 7.6 billion in 2019 to USD 20.1 billion by 2024, at a Compound Annual Growth Rate (CAGR) of 21.6% during the forecast period.
2.3 Data Processing
Data Processing is the component responsible for transforming and analyzing the data stored in the Data Lake. This step involves applying various processing techniques, such as data cleansing, data enrichment, and data aggregation, to derive meaningful insights from the raw data.
To process data in a Data Lake Architecture, organizations can utilize distributed processing frameworks like:
- Apache Spark: A fast and general-purpose distributed computing system for big data processing and analytics.
- Apache Flink: An open-source stream processing framework for distributed, high-performance, always-available, and accurate data streaming applications.
- Apache Hadoop MapReduce: A programming model for processing large datasets in parallel across a cluster of computers.
A survey by Syncsort found that 66% of organizations are using or planning to use Apache Spark for big data processing, while 53% are using or planning to use Apache Hadoop.
2.4 Data Governance and Security
Data Governance and Security are critical components of Data Lake Architecture, ensuring that data is managed, protected, and compliant with regulatory requirements. Data governance involves defining policies, standards, and procedures for data management, while data security focuses on protecting data from unauthorized access and ensuring data privacy.
Organizations can implement data governance and security measures in Data Lake Architecture by leveraging tools like:
- Apache Ranger: A security and governance framework for fine-grained access control and data protection in the Data Lake.
- Apache Atlas: A metadata management and governance tool for data discovery, lineage tracking, and data cataloging.
- Custom-built solutions: Tailored security and governance solutions based on specific organizational requirements.
According to a study by IBM, the average cost of a data breach in 2020 was $3.86 million, emphasizing the importance of robust data governance and security measures.
3. Benefits of Data Lake Architecture
Implementing Data Lake Architecture offers several benefits for organizations looking to leverage their data effectively. Some key benefits include:
Scalability: Data Lake Architecture provides the ability to scale storage and processing resources horizontally, allowing organizations to handle large volumes of data and accommodate future growth. A survey by ESG found that 63% of organizations cited scalability as a top reason for adopting Data Lake Architecture.
Flexibility: With Data Lake Architecture, organizations can store and analyze diverse data types without the need for predefined schemas, enabling flexibility in data exploration and analysis. This flexibility empowers data scientists and analysts to uncover new insights and drive innovation.
Cost-effectiveness: By leveraging cost-effective storage options like Hadoop HDFS or cloud storage services, organizations can significantly reduce their storage costs compared to traditional data warehouses. A study by Aberdeen Group found that organizations using Data Lake Architecture achieved a 50% reduction in data storage costs.
Data Integration: Data Lake Architecture allows organizations to integrate data from various sources, including structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data. This integration enables a holistic view of the data, facilitating comprehensive analysis and insights. According to a survey by TDWI, 82% of organizations consider data integration a critical component of their data management strategy.
Real-time Analytics: With Data Lake Architecture, organizations can perform real-time analytics on streaming data. This capability is particularly useful for industries like finance, e-commerce, and IoT, where real-time insights can drive immediate actions and decision-making. A report by MarketsandMarkets predicts that the real-time analytics market will grow from USD 6.9 billion in 2019 to USD 16.4 billion by 2024, at a CAGR of 19.1%.
4. Best Practices for Implementing Data Lake Architecture
Implementing Data Lake Architecture requires careful planning and execution. Here are some best practices to consider:
Define a Data Strategy: Before implementing Data Lake Architecture, organizations should define a clear data strategy that aligns with their business objectives. This strategy should outline the types of data to be stored, the desired analytics capabilities, and the governance and security requirements. According to a survey by NewVantage Partners, 98.8% of organizations believe that a data strategy is essential for driving business value.
Data Governance and Metadata Management: Establish robust data governance practices to ensure data quality, consistency, and compliance. Implement metadata management tools to track data lineage, understand data relationships, and enable efficient data discovery. A study by Gartner found that organizations with effective data governance practices achieve a 20% increase in data quality and a 15% reduction in data management costs.
Data Lake Security: Implement strong security measures to protect the Data Lake from unauthorized access and data breaches. This includes access controls, encryption, and monitoring mechanisms to detect and respond to security threats. According to a report by Ponemon Institute, the average cost of a data breach in 2020 was $3.86 million, emphasizing the importance of robust data security measures.
Data Cataloging and Data Lineage: Maintain a comprehensive data catalog that provides a clear understanding of the data stored in the Data Lake. Implement data lineage tracking to trace the origin and transformation of data, ensuring data integrity and auditability. A survey by Waterline Data found that organizations with a data catalog experienced a 50% reduction in time spent searching for data and a 30% increase in data analyst productivity.
Data Lake Optimization: Regularly monitor and optimize the performance of the Data Lake. This includes optimizing data storage formats, partitioning data for efficient querying, and leveraging data compression techniques to reduce storage costs. According to a study by Accenture, organizations that optimize their Data Lake can achieve up to 70% faster data processing and a 30% reduction in storage costs.
Collaboration and Knowledge Sharing: Foster a collaborative culture within the organization to encourage knowledge sharing and cross-functional collaboration. This can be achieved through data literacy programs, training sessions, and establishing data-driven decision-making processes. A survey by Gartner found that organizations with a data-driven culture are 2.5 times more likely to exceed their business goals.
5. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
5.1 What is the difference between a Data Lake and a Data Warehouse?
- A Data Lake is a storage repository that holds raw data in its native format, allowing for flexible exploration and analysis. In contrast, a Data Warehouse is a structured repository that stores data in a predefined schema, optimized for querying and reporting.
- Data Lakes are more suitable for handling diverse data types and exploratory analysis, while Data Warehouses are designed for structured data and business intelligence reporting.
5.2 How does Data Lake Architecture support big data analytics?
Data Lake Architecture supports big data analytics by providing a scalable and flexible infrastructure for storing and processing large volumes of data. With Data Lake Architecture, organizations can:
- Leverage distributed processing frameworks like Apache Spark and Apache Hadoop to perform complex analytics on massive datasets.
- Store raw data, allowing for iterative analysis and the application of advanced analytics techniques like machine learning and predictive modeling.
- Enable real-time analytics on streaming data, providing valuable insights for industries like finance, e-commerce, and IoT.
5.3 What are the challenges of implementing Data Lake Architecture?
Implementing Data Lake Architecture can come with some challenges, including:
Data Quality: Ensuring data quality can be challenging, as Data Lakes store raw and unprocessed data. Organizations need to implement data governance practices and data cleansing techniques to maintain data integrity.
Data Governance and Security: Data governance and security are crucial aspects of Data Lake Architecture. Organizations need to establish robust governance policies, access controls, and encryption mechanisms to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance.
Data Integration: Integrating data from various sources can be complex, as different data formats and structures need to be harmonized. Organizations need to invest in data integration tools and technologies to streamline this process.
Data Discovery and Cataloging: With large volumes of data stored in the Data Lake, discovering and cataloging relevant data can be challenging. Implementing metadata management tools and data cataloging practices can help address this challenge.
5.4 How can data governance be ensured in a Data Lake?
Data governance in a Data Lake can be ensured by:
- Defining clear data governance policies and standards.
- Establishing data stewardship roles and responsibilities to oversee data quality and compliance.
- Implementing access controls and permissions to restrict data access based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Implementing data lineage tracking to understand the origin and transformation of data.
- Conducting regular data audits and assessments to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements.
- Providing data governance training and awareness programs to educate employees about their responsibilities in maintaining data integrity and security.
5.5 What are some popular tools for implementing Data Lake Architecture?
There are several popular tools and technologies available for implementing Data Lake Architecture, including:
Apache Hadoop: An open-source framework that provides distributed storage and processing capabilities for big data analytics.
Apache Spark: A fast and general-purpose distributed computing system that supports in-memory processing and advanced analytics.
Amazon S3: A scalable and secure object storage service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS).
Azure Data Lake Storage: A scalable and secure data lake storage service provided by Microsoft Azure.
Google Cloud Storage: A scalable and cost-effective object storage service provided by Google Cloud Platform.
Apache Kafka: A distributed streaming platform that enables real-time data ingestion and processing.
Apache NiFi: An open-source data integration tool that facilitates data ingestion, transformation, and routing.
Apache Ranger: A security and governance framework that provides fine-grained access control and data protection for the Data Lake.
Apache Atlas: A metadata management and governance tool that enables data discovery, lineage tracking, and data cataloging.
These are just a few examples, and there are many other tools and technologies available in the market to suit specific organizational needs and requirements.
6. Real-World Success Stories
Many organizations have successfully implemented Data Lake Architecture and achieved significant benefits. Here are a few real-world success stories:
Netflix: Netflix leverages Data Lake Architecture to store and analyze massive volumes of data generated by its streaming platform. By processing and analyzing this data, Netflix gains insights into user preferences, content popularity, and viewing patterns, enabling personalized recommendations and driving business growth. Netflix’s Data Lake processes over 500 billion events per day, empowering data-driven decision-making across the organization.
Uber: Uber utilizes Data Lake Architecture to store and analyze data from millions of rides and driver interactions. By leveraging big data analytics, Uber optimizes route planning, demand forecasting, and dynamic pricing, resulting in improved customer experience and operational efficiency. Uber’s Data Lake handles petabytes of data, enabling real-time analytics and machine learning applications.
Airbnb: Airbnb employs Data Lake Architecture to store and analyze data from its global platform, including booking information, user reviews, and host profiles. By leveraging this data, Airbnb enhances its search algorithms, personalizes user experiences, and detects fraudulent activities. Airbnb’s Data Lake enables data-driven decision-making, leading to increased customer satisfaction and business growth.
These success stories demonstrate the transformative power of Data Lake Architecture in enabling organizations to harness the value of their data and drive innovation.
7. Future of Data Lake Architecture
As data continues to grow exponentially and the need for advanced analytics intensifies, the future of Data Lake Architecture looks promising. Here are some emerging trends and developments in the field:
Cloud-based Data Lakes: With the increasing adoption of cloud computing, more organizations are moving their Data Lakes to the cloud. Cloud-based Data Lakes offer scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness, enabling organizations to leverage the power of the cloud for data storage and processing.
Serverless Data Lakes: Serverless computing is gaining traction in the Data Lake ecosystem. Serverless Data Lakes allow organizations to focus on data analysis and insights without worrying about infrastructure management. Serverless architectures enable automatic scaling, cost optimization, and simplified data processing.
AI and Machine Learning Integration: The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with Data Lake Architecture is becoming increasingly common. AI and ML algorithms can be applied to the vast amounts of data stored in the Data Lake, enabling advanced analytics, predictive modeling, and automated insights discovery.
Real-time Analytics: The demand for real-time analytics is growing, and Data Lake Architecture is evolving to support this need. Real-time data ingestion, stream processing, and low-latency querying capabilities are being integrated into Data Lake architectures to enable real-time decision-making and actionable insights.
Data Mesh Architecture: Data Mesh is an emerging architectural paradigm that extends the principles of Data Lake Architecture. It focuses on decentralizing data ownership and enabling domain-driven data management. Data Mesh aims to create a self-serve data infrastructure where data is treated as a product and owned by domain teams, fostering agility and scalability.
As organizations continue to realize the value of data-driven insights, the adoption of Data Lake Architecture is expected to grow. The future of Data Lake Architecture looks promising, with advancements in cloud computing, serverless architectures, AI integration, real-time analytics, and emerging paradigms like Data Mesh.
8. Conclusion
Data Lake Architecture is a powerful framework that enables organizations to store, process, and analyze large volumes of diverse data. By leveraging the components of Data Ingestion, Data Storage, Data Processing, and Data Governance, organizations can unlock valuable insights
Read more our Data Architecture related articles on Blog
Find more about our conprehensive Data Architecture Guide