The Ultimate Guide to Business Process Modeling
The Ultimate Guide to Business Process Modeling
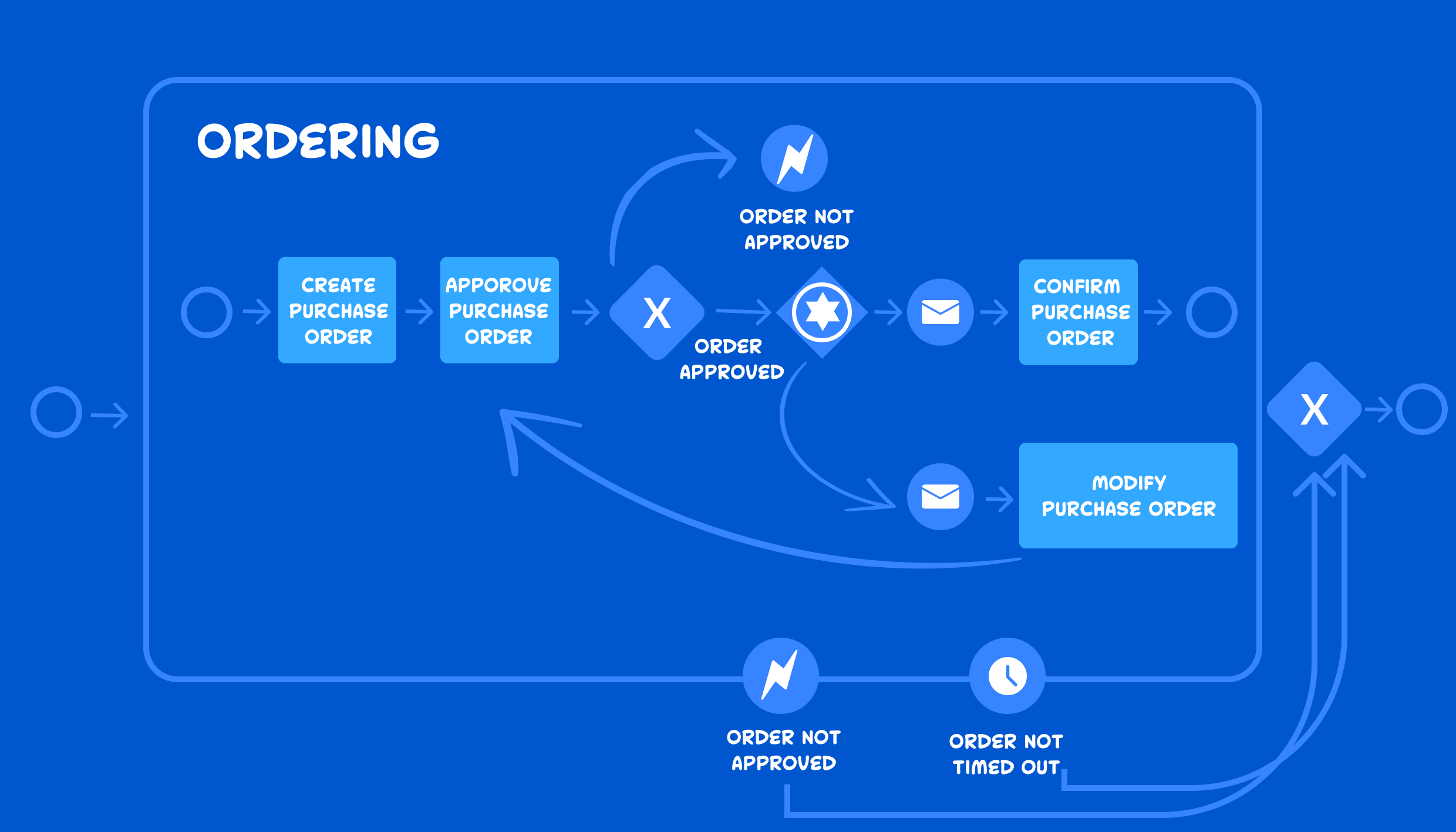
In today’s rapidly evolving business landscape, organizations are constantly seeking ways to optimize their operations and maximize productivity. One powerful tool that has emerged to address this need is Business Process Modelling (BPM). BPM is a systematic approach to analyzing, designing, implementing, and managing business processes to improve performance and achieve organizational goals. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the intricacies of BPM, its benefits, and how it can revolutionize the way businesses operate.
Table of Contents
- Introduction to Business Process Modelling
- The Importance of Business Process Modelling
- Key Components of Business Process Modelling
- Benefits of Implementing Business Process Modelling
- Steps to Implement Business Process Modelling
- Best Practices for Successful Business Process Modelling
- Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of BPM Implementation
- Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Business Process Modelling
- Conclusion
1. Introduction to Business Process Modelling
Business Process Modelling (BPM) is a methodology that enables organizations to analyze, map, and optimize their business processes. It involves the use of various techniques and tools to create visual representations of processes, identify inefficiencies, and propose improvements. BPM provides a holistic view of how different processes within an organization interact and enables stakeholders to make informed decisions for process optimization.
2. The Importance of Business Process Modelling
Efficient business processes are the backbone of any successful organization. By implementing BPM, businesses can gain a comprehensive understanding of their existing processes, identify bottlenecks, and streamline operations. BPM enables organizations to:
- Enhance operational efficiency: By analyzing and optimizing business processes, organizations can eliminate redundant steps, reduce errors, and improve overall efficiency.
- Improve decision-making: BPM provides stakeholders with a clear visual representation of processes, enabling them to make data-driven decisions and identify areas for improvement.
- Foster collaboration: BPM facilitates communication and collaboration among different departments and stakeholders, leading to better coordination and alignment of goals.
- Adapt to change: In today’s dynamic business environment, organizations need to be agile and adaptable. BPM allows businesses to quickly identify and modify processes to meet changing market demands.
- Achieve cost savings: By eliminating inefficiencies and optimizing processes, organizations can reduce costs associated with manual errors, rework, and resource allocation.
3. Key Components of Business Process Modelling
BPM consists of several key components that work together to create a comprehensive framework for process optimization. These components include:
a. Process Identification and Documentation
The first step in BPM is to identify and document all the processes within an organization. This involves mapping out the sequence of activities, inputs, and outputs for each process. Process documentation provides a clear understanding of how different processes contribute to the overall value chain.
b. Process Analysis
Once the processes are identified and documented, the next step is to analyze them. Process analysis involves identifying bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. Various techniques such as value stream mapping, root cause analysis, and process flow analysis are used to gain insights into process performance.
c. Process Design and Optimization
Based on the analysis, organizations can design and optimize their processes to improve efficiency and effectiveness. This may involve redesigning workflows, automating manual tasks, or reassigning responsibilities. The goal is to create streamlined processes that minimize waste and maximize value creation.
d. Process Implementation and Monitoring
After the design phase, the optimized processes are implemented and monitored. This involves training employees, updating standard operating procedures, and establishing performance metrics. Regular monitoring allows organizations to track process performance and make necessary adjustments.
e. Continuous Improvement
BPM is an iterative process that requires continuous improvement. Organizations should regularly review and refine their processes to adapt to changing business needs and market conditions. Continuous improvement ensures that processes remain efficient and aligned with organizational goals.
4. Benefits of Implementing Business Process Modelling
Implementing BPM offers numerous benefits to organizations across various industries. Some key benefits include:
- Enhanced efficiency and productivity: By optimizing processes, organizations can reduce cycle times, eliminate bottlenecks, and improve overall productivity.
- Improved customer satisfaction: Streamlined processes lead to faster response times, better quality products/services, and ultimately, increased customer satisfaction.
- Cost savings: BPM helps identify and eliminate unnecessary steps, reduce rework, and optimize resource allocation, resulting in significant cost savings.
- Better decision-making: BPM provides stakeholders with a clear understanding of processes, enabling them to make informed decisions and prioritize improvement initiatives.
- Enhanced collaboration and communication: BPM promotes cross-functional collaboration and communication, leading to better alignment and coordination among teams and departments.
5. Steps to Implement Business Process Modelling
Implementing BPM requires a systematic approach. Here are the key steps involved in implementing BPM:
-
Identify and document all the processes within the organization. This involves mapping out the sequence of activities, inputs, and outputs for each process.
-
Analyze the processes to identify bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and areas for improvement. Use techniques such as value stream mapping, root cause analysis, and process flow analysis to gain insights into process performance.
-
Design and optimize the processes based on the analysis. This may involve redesigning workflows, automating manual tasks, or reassigning responsibilities. The goal is to create streamlined processes that minimize waste and maximize value creation.
-
Implement the optimized processes and monitor their performance. This includes training employees, updating standard operating procedures, and establishing performance metrics. Regular monitoring allows organizations to track process performance and make necessary adjustments.
-
Continuously improve the processes. Regularly review and refine the processes to adapt to changing business needs and market conditions. Continuous improvement ensures that processes remain efficient and aligned with organizational goals.
6. Best Practices for Successful Business Process Modelling
To ensure successful implementation of BPM, organizations should follow these best practices:
- Clearly define the objectives and scope of the BPM initiative.
- Involve key stakeholders from different departments to gain diverse perspectives.
- Use standardized notation and modeling techniques to ensure consistency and clarity.
- Regularly communicate and collaborate with stakeholders to ensure buy-in and alignment.
- Prioritize improvement initiatives based on their impact and feasibility.
- Provide adequate training and support to employees involved in the BPM initiative.
- Continuously monitor and measure process performance to track improvements.
- Foster a culture of continuous improvement and innovation within the organization.
7. Case Studies: Real-Life Examples of BPM Implementation
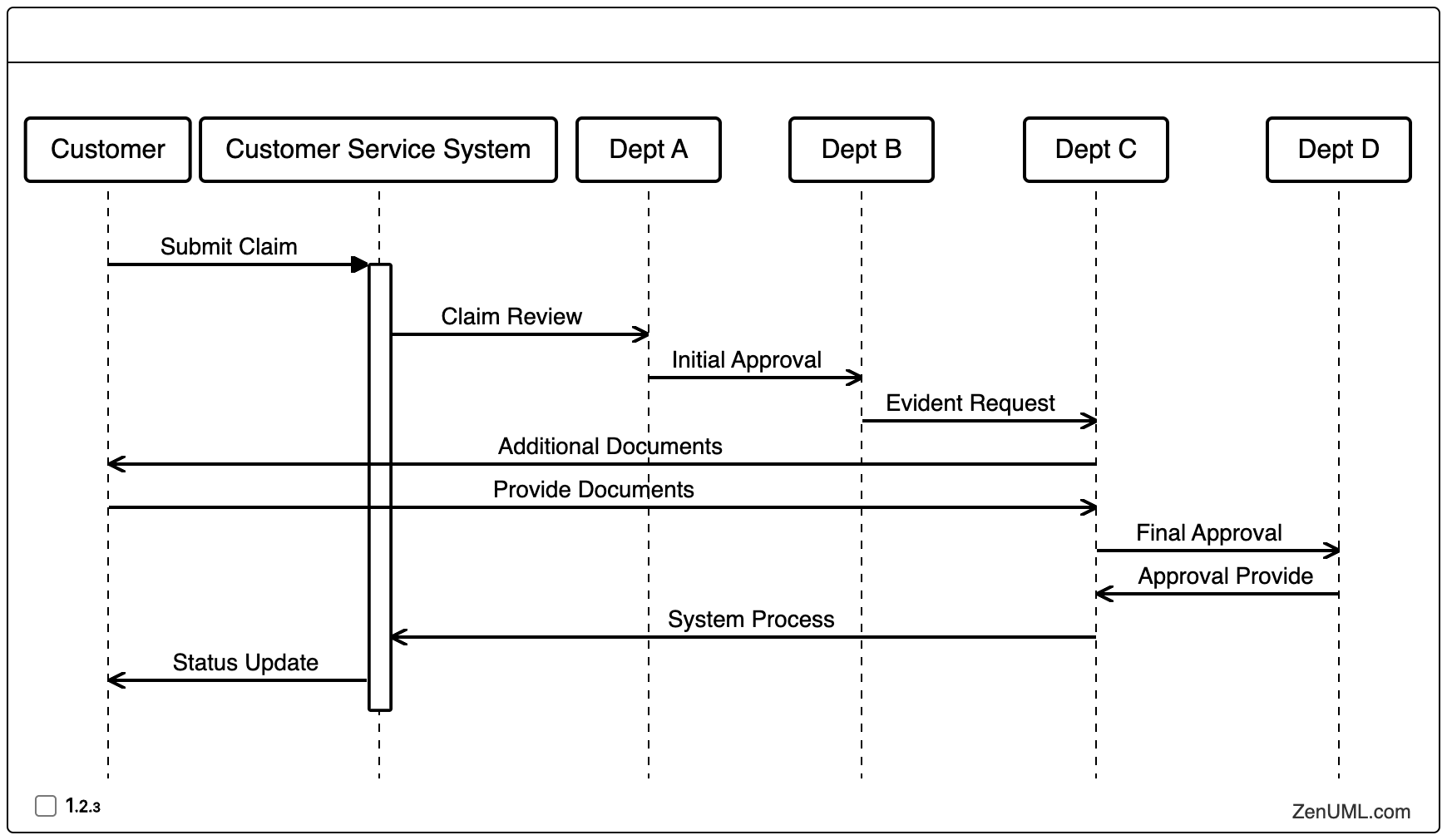
Find more on Business Workflow Analysis with Sequence Diagrams
Find more on Use Sequence Diagram to Improve Business Process
8. Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ) about Business Process Modelling
Q1: What is the role of technology in BPM?
A1: Technology plays a crucial role in BPM by enabling process automation, data analysis, and real-time monitoring. BPM software tools provide organizations with the necessary capabilities to model, simulate, and optimize their processes.
Q2: How long does it take to implement BPM?
A2: The timeline for implementing BPM varies depending on the size and complexity of the organization. It can range from a few months to a year or more. It is important to note that BPM is an ongoing process that requires continuous improvement.
Q3: How can BPM help with compliance and risk management?
A3: BPM enables organizations to document and standardize their processes, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements. It also helps identify and mitigate risks by providing visibility into process dependencies and potential vulnerabilities.
Q4: Can BPM be applied to any industry?
A4: Yes, BPM can be applied to any industry. The principles and techniques of BPM are applicable across various sectors, including manufacturing, healthcare, finance, and retail.
Q5: What are the key challenges in implementing BPM?
A5: Some key challenges in implementing BPM include resistance to change, lack of stakeholder buy-in, and the complexity of mapping and analyzing processes. However, with proper planning, communication, and support, these challenges can be overcome.
9. Conclusion
Business Process Modelling is a powerful methodology that enables organizations to optimize their operations, improve efficiency, and achieve their goals. By analyzing, designing, implementing, and continuously improving their processes, businesses can stay competitive in today’s fast-paced business environment. Implementing BPM requires a systematic approach, involving process identification, analysis, design, implementation, and continuous improvement. By following best practices and leveraging technology, organizations can unlock the full potential of BPM and drive sustainable growth. Embrace the power of BPM and revolutionize your business today!
Find more about our conprehensive Enterprise Architecture Guide
Find more about our framework guide on Framework Docs
Find more about Enterprise Achitecture Tools